Taxation is a natural form of tax which the government uses as a guaranteed income from which they finance public services, social amenities, maintaining law and order, etc.
Taxes are broadly classified into two categories which are direct tax and indirect tax in india.It is essential for the population, companies and authorities to distinguish between these two types of taxes, their consequences and their functions in the economy.
It is very important for a person living in our country to know about direct tax and indirect tax in India because everyone has to think about direct and indirect taxes sometimes in their daily life, so if you are aware of all the taxes.
Therefore, if you already know about it then you will see that you will never have to face any kind of problem.
So in this blog post we have described in detail all the aspects of direct and indirect taxes in India like their major types, advantages and disadvantages, features and explained all in brief.
Difference Between Direct and Indirect Taxes

Now we will understand what is the difference between direct tax and indirect tax in India so that you can understand even the smallest thing about these taxes:
Direct Taxes in India

Presently we will discuss in detail about direct taxes in India in which its overall types, advantages and disadvantages have been understood in the paragraphs below.
What is the Definition of Direct Taxes
The direct taxes in india are the taxes that are charged directly on the persons and the organizations and are paid right to the treasury.
Direct taxes cannot be shifted to another person and this implies that the cost of meeting the tax lies on the individual or organization charged with payment of the tax.
Direct tax is progressive in nature due to which, rate of tax rises as the taxable amount rises.
This characteristic in particular aids in the lessening of income disparity because the tax rate is higher corresponding to the amounts that the well-off can contribute.
Various Types of Direct Taxes

You all must be knowing very well that there are all various types of direct taxes, out of which we have filtered the main taxes and decided to present them before you all.
- Income Tax: Income tax is one of the most prevalent direct tax systems across India. It applies to income earned by individuals, Hindu Undivided Families (HUFs), firms and corporations. The Income Tax Act 1961 is the principal law providing for the incidence, assessment and collection of income tax in India.
- Corporate Tax: Corporate tax is charged on the income that has been generated by any corporation or company. This tax is also regulated by the income tax act of the year 1961. Depending on the size and residence status of the company, the scale of corporate tax is set at a certain rate.
- Wealth tax: Wealth tax means the direct tax which was in force starting from the year 2005 and it has been abolished from the Financial Year 2015-16, this tax has been charged on the total net wealth possessed by each individual, Hindu undivided family or company.
- Capital gains Tax: This tax is paid on profits earned from the disposal of assets called capital assets including land, shares and securities. From the tax point of view, there are short-term gains and long-term gains, where each is taxed separately.
- Securities Transaction Tax (STT): STT is another tax which is imposed on securities including, shares, derivatives, and equity oriented mutual fund schemes traded in the stock exchange. It is gotten at the time of making the sale and is applies to both the buyer and the seller.
- Dividend Distribution Tax (DDT): Tax on corporation for any sum stated, paid or issuing as dividend to the shareholders.
- Property Tax: Property tax is a special kind of charge that is placed locally by the government on properties that includes building and lands. It provides funding to public service as schools and infrastructure for the amount of the properties’ value.
Advantages and Disadvantages Direct Taxes
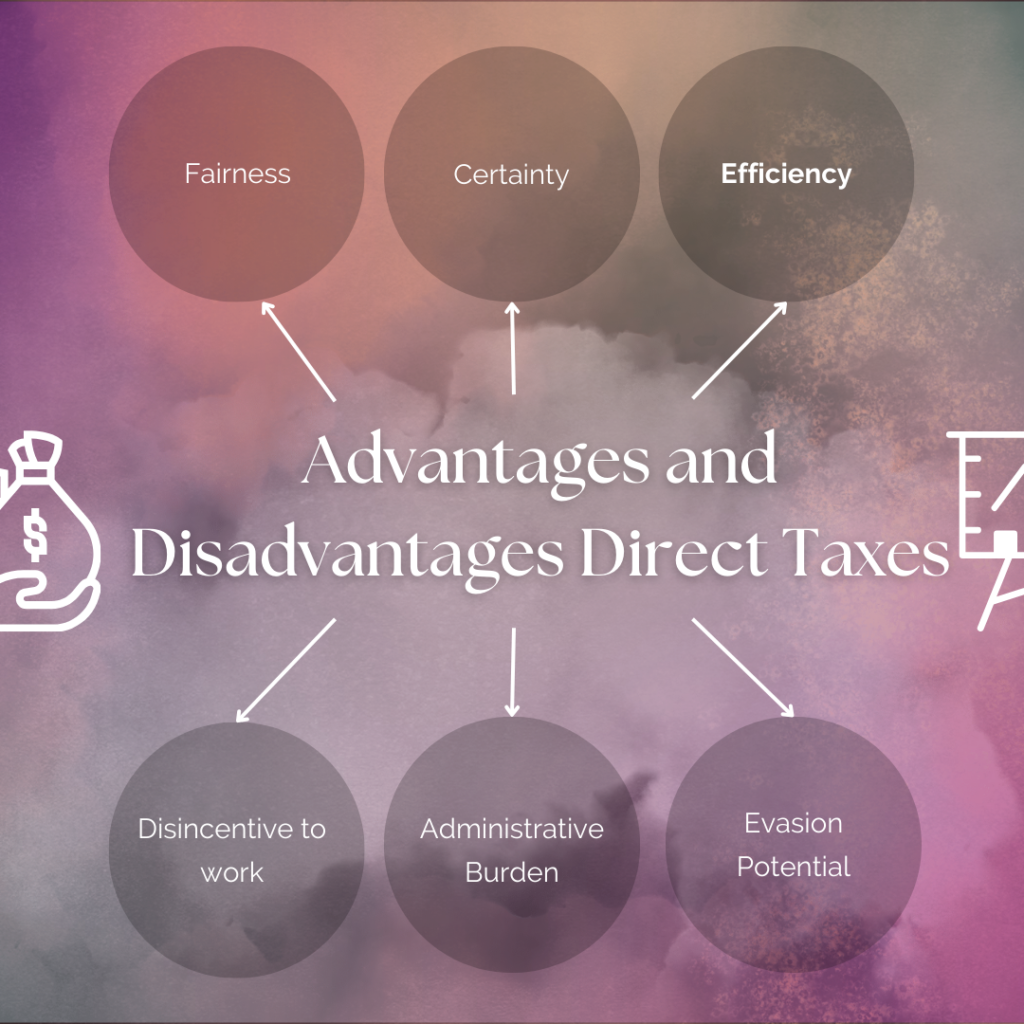
The government of our country gets many more benefits and drawbacks through taxation, similarly the government can also see the advantages and disadvantagves of direct taxes, about which we have summarized all in detail in a concise table:
| Advantages of Direct Taxes | Disadvantages of Direct Taxes |
| Fairness: Taxes are based on income | Disincentive to work: High tax rates may discourage individuals from working harder |
| Certainty: Tax liabilities are clear and predictable for taxpayers | Administrative Burden: Complex tax laws can lead to compliance costs |
| Efficiency: Relatively low collection costs compared to indirect taxes | Evasion Potential: Taxpayers may find ways to avoid or minimize tax payments |
| Economic Stability: Can be used to regulate income and control inflation | Economic Growth Impact: High taxes can hinder economic growth and investment |
| Progressive: Can reduce income inequality by redistributing wealth | Political Interference: Tax policies can be influenced by political considerations |
In lastly we would like to tell you direct tax is the 1st most important tax among of direct tax and indirect tax in india.
Indirect Taxes in India

Presently we will discuss in detail about indirect taxes in India in which its overall types, advantages and disadvantages have been understood in the paragraphs below.
What is the Definition of Indirect Taxes?

Indirect taxes are taxes that are levied only on goods and services rather than on income or profits.
Indirect taxes are the exact opposite of direct taxes and the overall burden of indirect taxes can very easily be passed on to another person or entity, usually the last consumer.
Indirect taxes are considered to be highly regressive in nature in India, meaning that they take a much larger percentage of the income of low income individuals compared to high income individuals.
However, they are considered much easier to administer and collect because they are considered inherent to goods and services.
Different Types of Indirect Taxes

You all must be knowing very well that there are all different types of indirect taxes, out of which we have filtered the major taxes and decided to present them before you all.
- Goods and Services Tax (GST): A comprehensive tax on the supply of goods and services, usually levied at each stage of the supply chain, with credit for taxes paid on inputs.
- Customs Duty: This is a tax that is imposed on goods imported into a country, the main purpose of which is to protect domestic industries and increase revenue.
- Excise Duty: A direct charge that is imposed on certain products commonly known as sin products which include alcohol, tobacco, and fuel.
- Service Tax: A charge that is placed on service provision, frequently replaced or integrated into the GST system in many countries.
- Value Added Tax (VAT): VAT, just like GST, is also an indirect tax which works on the principle of value added tax throughout the manufacturing process or supply chain.
- Stamp Duty: An informal or conventional duty that is commonly associated with the selling of property, stocks or bonds, or any similar assets.
- Entertainment Tax: Something like a consumption tax on entertainment such as going to the theatres or watching movies, shows, or spending some time at amusement parks.
- Luxury Tax: This is a levy on goods and services that are expensive or considered to be luxuries for instance jewelries, expensive cars among others.
- Sin Tax: An indirect tax that is levied on specified products which have adverse effects on the society such as cigarettes, wines and lotteries.
- Import and Export Duties: The charges collected on imported and exported products these are somewhat like the customs duties but can include other charges as well.
- Sales Tax: A kind of tax levied on products and services, where it is normally integrated into the price of the product at the time of sale.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Indirect Taxes
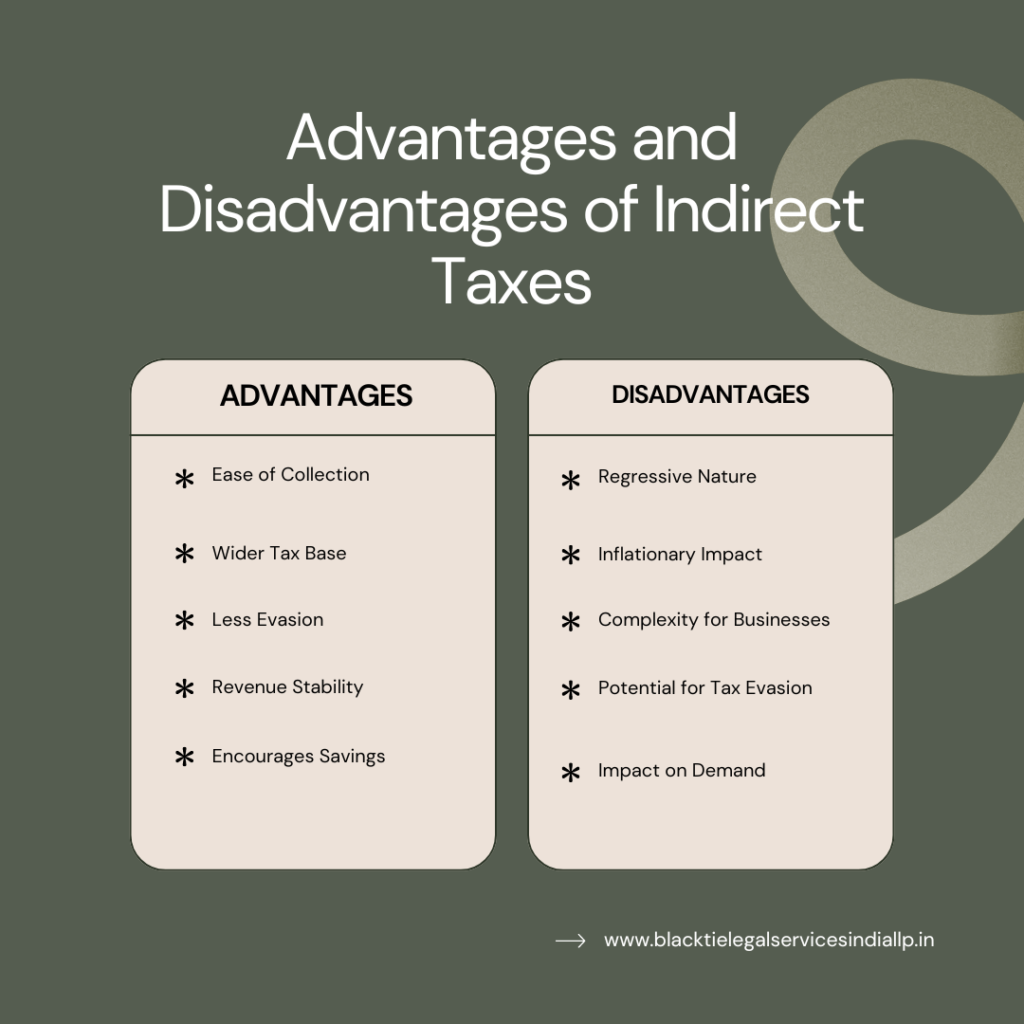
There are several advantages and disadvantages of indirect taxes which we have summarized in detail in the table below:
| Advantages of Indirect Taxes | Disadvantages of Indirect Taxes |
| Ease of Collection: Indirect taxes are comparatively easier to be collected because they are charged with the price of the commodities and services. | Regressive Nature: The second type of taxes, the indirect ones, are deemed regressive in as much as they provide higher impacts to poor population groups. |
| Wider Tax Base: This system of taxation is whereby consumers are taxed practically on most of the goods and services they consume, and therefore every one who consumes goods and services that are deemed to be subject to indirect taxes does contribute to the taxes that fund the government . | Inflationary Impact: Because indirect taxes are borne by the consumers there have social implications; one of these is the potential to increase the price of goods and services, thus inflation. |
| Less Evasion: Indirect taxes are almost imbedded in the transactions and therefore it is difficult to avoid them. | Complexity for Businesses: While consumers benefit from simplicity, businesses face the administrative burden of calculating, collecting, and remitting indirect taxes. |
| Revenue Stability: Indirect taxes are related to consumption and since consumption has a more stable tendency in comparison with income or profit, it is possible to state that these taxes are more favorable. | Potential for Tax Evasion: Despite being harder to evade, indirect taxes can still be avoided through practices such as smuggling or underreporting sales. |
| Encourages Savings: These are based on the consumption level rather than savings and investment and thus are not savings-investment distorting taxes. | Impact on Demand: Higher indirect taxes on goods and services can reduce demand, especially for non-essential items. |
In lastly we would like to tell you direct tax is the 1st most important tax among of direct tax and indirect tax in india.
In Conclusion

Both direct tax and indirect tax in india plays an important role in the economy and fiscal system of our country.
Direct taxes go a long way in ensuring that wealthy individuals and businesses contribute as much as possible to the public coffers while promoting social equality.
On the other hand, indirect taxes are considered much more important for revenue generation and are much easier to manage and collect.
All these are very important to maintain the balance between direct tax and indirect tax to promote development and to ensure that the burden of these taxes is distributed evenly.
Therefore, we have done thorough research and provided all the information about direct tax and indirect tax in India for all of you in this blog post and finally we hope that you will get relief from any kind of complexity in this blog post.
FAQs
Q1. Is GST a direct or indirect tax?
A1. GST is an indirect tax
It’s a tax levied on the consumption of goods and services, and the burden is typically passed on to the end consumer by the businesses involved in the supply chain.
Q2. How is VAT calculated?
A2. VAT (Value Added Tax) is calculated by subtracting the input tax (tax paid on purchases) from the output tax (tax collected on sales).
Q3. How to GST calculate?
A3. GST (Goods and Services Tax) is calculated based on the taxable value of goods or services and the applicable GST rate.
Q4. What is the TDS limit?
A4. The TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) limit varies depending on the type of payment.


Add a Comment