
For Applying GST Registration Click Here…
Introduction to Export GST Rules
Export plays a vital role in India’s economy, and to support exporters, the government has introduced specific Export GST rules under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) law. These rules are designed to ensure that exports remain tax-free and competitive in the global market while maintaining proper compliance within the GST framework.
Under GST, exports are treated as zero-rated supplies, which means no GST burden should ultimately fall on the exporter. However, to claim this benefit, exporters must strictly follow the applicable Export GST rules, including registration, documentation, filing of returns, and refund procedures. Whether you are exporting goods or services, understanding these rules is essential to avoid delays, penalties, or rejection of refunds.
Many exporters face issues not because GST is complex, but because they are unaware of the correct Export GST rules or fail to follow them properly. From choosing between LUT or IGST payment to ensuring accurate invoice details, every step matters.

What Are Export GST Rules Under GST Law?
The Export GST rules under GST law define how exports of goods and services are treated for taxation purposes in India. As per the GST framework, exports are considered zero-rated supplies, meaning that no GST should be charged on export transactions. The objective of these rules is to ensure that Indian exporters are not burdened with domestic taxes while competing in international markets.
According to the Export GST rules, an exporter has two options while making exports. The first option is to export goods or services without payment of GST by furnishing a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) or a Bond. The second option is to export with payment of IGST and later claim a refund of the tax paid. These options give flexibility to exporters based on their cash flow and compliance preferences.
The Export GST rules also clearly define what qualifies as an export under GST law. In the case of goods, the goods must be taken out of India to a place outside the country. For services, certain conditions must be fulfilled, such as the supplier being located in India, the recipient being located outside India, and payment being received in foreign currency.
To ensure transparency and compliance, the Export GST rules require exporters to maintain proper documentation, including tax invoices, shipping bills, export general manifests, and foreign remittance certificates. Failure to comply with these rules may lead to rejection of refunds or penalties under GST law.
Overall, the Export GST rules under GST law aim to promote exports by eliminating tax costs while ensuring that exporters follow a structured and compliant process. Understanding these rules helps exporters avoid mistakes and smoothly manage their export-related GST obligations.

Export GST Rules for Zero-Rated Supplies
Under GST, exports are given special treatment to ensure that Indian exporters remain competitive in the global market. As per the Export GST rules, exports fall under the category of zero-rated supplies, which means that the tax rate on such supplies is effectively zero, even though they are taxable under GST law.
According to the Export GST rules, zero-rated supplies include two main categories:
Export of goods or services outside India
Supply of goods or services to a Special Economic Zone (SEZ) unit or developer
This zero-rating ensures that exporters do not bear the burden of GST on their outward supplies. However, it is important to note that zero-rated supplies are different from exempt supplies. While exempt supplies do not attract GST, zero-rated supplies allow exporters to claim a refund of input tax credit (ITC), which is a major benefit under the Export GST rules.
The Export GST rules provide exporters with two methods to handle zero-rated supplies. Exporters can either supply goods or services without payment of GST by filing a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) or Bond, or they can export with payment of IGST and later claim a refund of the tax paid. Both methods are legally valid, and the choice depends on the exporter’s working capital and compliance strategy.
To avail the benefits of zero-rated supplies, exporters must strictly follow the Export GST rules, including proper invoicing, timely filing of GST returns, and maintaining export-related documents. Any mismatch in details or non-compliance may result in delays or rejection of refunds.

Export GST Rules Without Payment of Tax (LUT/Bond)
The Export GST rules allow exporters to supply goods or services outside India without paying GST at the time of export by submitting a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) or a Bond. This option is widely preferred by exporters as it helps in saving working capital and avoids the hassle of claiming refunds of IGST later.
As per the Export GST rules, a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) can be furnished by eligible exporters who have not been prosecuted for tax evasion beyond the prescribed limit under GST law. The LUT is submitted electronically on the GST portal and is generally valid for one financial year. Once the LUT is approved, exporters can make zero-rated supplies without charging GST on their export invoices.
In cases where an exporter is not eligible to furnish an LUT, the Export GST rules require the submission of a Bond along with a bank guarantee. The bond ensures that the exporter will comply with GST regulations and complete the export within the prescribed time. If the export is not completed or foreign remittance is not received within the allowed period, GST becomes payable along with applicable interest.
Under the Export GST rules, exporters opting for LUT or Bond must clearly mention on the invoice that the supply is made under LUT or Bond without payment of tax. They must also ensure timely filing of GST returns and proper maintenance of export documents to avoid compliance issues.
Overall, the Export GST rules for export without payment of tax through LUT or Bond are designed to simplify export procedures and ease cash flow pressure. When followed correctly, this method offers a smooth and efficient way to carry out export transactions under GST.
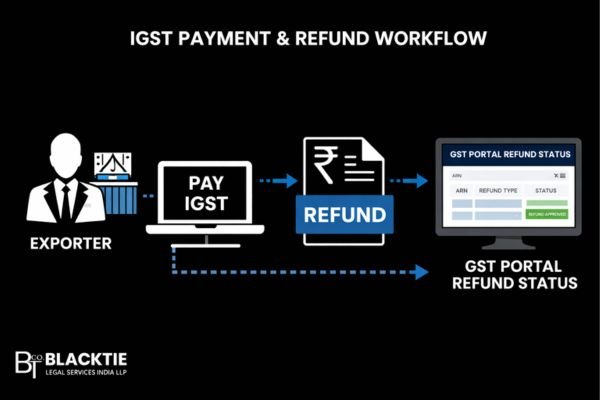
Export GST Rules With Payment of IGST
Under the Export GST rules, exporters are also given the option to export goods or services after paying Integrated GST (IGST) and then claim a refund of the tax paid. This method is often chosen by exporters who are unable to furnish a Letter of Undertaking (LUT) or who prefer a straightforward refund mechanism.
As per the Export GST rules, when exporters opt for payment of IGST, the tax is charged on the export invoice at the applicable IGST rate. Once the goods are exported or services are provided, the exporter can apply for a refund of the IGST paid. In the case of goods, the shipping bill itself is treated as a refund application, provided that all GST returns are filed correctly.
The Export GST rules require accurate matching of invoice details, shipping bill data, and GST return filings such as GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B. Any mismatch in these details can delay the refund process. For export of services, the refund application must be filed separately along with proof of export and receipt of foreign currency.
While this option ensures compliance under the Export GST rules, it may temporarily block the exporter’s working capital until the refund is received. Therefore, exporters should carefully evaluate their cash flow position before choosing to export with payment of IGST.
Documents Required Under Export GST Rules
Proper documentation is the backbone of GST compliance for exporters. Under the Export GST rules, maintaining accurate and complete documents is essential to prove that a transaction qualifies as an export and to claim benefits such as zero-rating and GST refunds.
As per the Export GST rules, exporters must issue a tax invoice containing all mandatory details, including GSTIN, invoice number, date, description of goods or services, and a declaration that the supply is made for export. In case of exports without payment of tax, the invoice should clearly mention that it is issued under LUT or Bond.
For export of goods, key documents required under the Export GST rules include the shipping bill, bill of export, and Export General Manifest (EGM) filed with Customs. These documents act as proof that the goods have physically moved outside India and are crucial for processing IGST refunds.
In the case of export of services, the Export GST rules require documents such as the contract or agreement with the foreign client, invoice, and Foreign Inward Remittance Certificate (FIRC) or bank realization certificate as proof of receipt of payment in foreign currency.
Additionally, exporters must keep copies of LUT or Bond, GST return filings (such as GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B), and refund applications wherever applicable. Any mismatch or missing document can result in delay or rejection of refund claims under the Export GST rules.
Export GST Rules for GST Refund Claims
One of the biggest benefits available to exporters under GST is the refund mechanism. The Export GST rules for GST refund claims are designed to ensure that exporters do not bear the burden of GST on zero-rated supplies. However, to receive refunds smoothly, exporters must strictly follow the prescribed rules and procedures.
As per the Export GST rules, exporters can claim GST refunds under two situations. First, when exports are made without payment of tax under LUT or Bond, exporters can claim a refund of unutilized Input Tax Credit (ITC). Second, when exports are made with payment of IGST, exporters are eligible to claim a refund of the IGST paid on such exports.
The Export GST rules require exporters to file GST returns accurately and on time for refund eligibility. Details furnished in GSTR-1 must match with shipping bill data and GSTR-3B filings. Even minor mismatches in invoice values, GSTIN, or tax amounts can lead to delays or rejection of refund claims.
For export of goods, the Export GST rules treat the shipping bill as a deemed refund application, provided that the Export General Manifest (EGM) is filed and GST returns are properly submitted. In the case of export of services, exporters must file a separate refund application along with proof of export and evidence of foreign currency realization.
Additionally, exporters must adhere to timelines specified under the Export GST rules. Refund applications should be filed within the prescribed period, and all supporting documents must be maintained to respond to any queries raised by tax authorities.
Common Mistakes While Following Export GST Rules
Even though the Export GST rules are designed to support exporters, many businesses face compliance issues due to avoidable mistakes. These errors often lead to refund delays, notices from the GST department, or even financial losses. Understanding common pitfalls can help exporters stay compliant and stress-free.
One of the most common mistakes under the Export GST rules is not filing or renewing the LUT on time. Many exporters continue to export without realizing that the LUT is valid only for one financial year. Exporting without a valid LUT may result in tax liability along with interest.
Another frequent error is incorrect or incomplete invoice details. Under the Export GST rules, export invoices must contain specific declarations and accurate values. Mismatches between invoices, shipping bills, and GST returns such as GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B often cause refund rejections or delays.
Exporters also make the mistake of choosing the wrong export option—such as paying IGST when LUT could have been used, or vice versa—without evaluating cash flow impact. A poor understanding of the Export GST rules can unnecessarily block working capital.
In the case of export of services, many exporters fail to receive payment in foreign currency within the prescribed time, which is mandatory under the Export GST rules. This can result in denial of zero-rated benefits and refund claims.
Lastly, improper documentation and late filing of returns remain major compliance issues. Missing FIRCs, incorrect shipping bill data, or delayed GST return filing can all disrupt refund processing under the Export GST rules.
Latest Updates in Export GST Rules
The landscape of Export GST rules is constantly evolving as the government continues to refine GST procedures to make exports easier, faster, and more competitive for Indian exporters. Here are some of the latest updates and reforms that every exporter should know in 2025:
📌 Faster and Easier GST Refunds
Recently, the GST Council has approved measures to speed up export GST refund claims, especially for small amounts under ₹1,000. This means that exporters with small refunds — common in courier and postal exports — can expect quicker processing and faster liquidity.
The Economic Times
📌 Export Status for More Services
The GST Council and tax authorities have recommended changes in place of supply rules for intermediary services, where services provided to clients outside India will now more clearly qualify as exports. This reform aims to align Export GST rules with international norms and reduce disputes, particularly for service exporters like IT/ITES firms.
The Economic Times
+1
📌 Provisional Refunds for Exporters
From 1 November 2025, exporters can benefit from 90% provisional refunds of GST on zero-rated supplies based on system-driven risk assessment. This update helps improve cash flow for exporters by reducing delays in refund processing.
PwC
📌 No Minimum Export Refund Threshold
The GST Council has recommended changes to remove the minimum refund threshold for exports made with GST payment — a big relief for small exporters using postal or courier services. This change is designed to help smaller players claim refunds without being blocked by limits that previously applied.
Goods and Services Tax Council
📌 Simplified GST Registration Process
Although not limited to exports alone, simplified GST registration schemes for small and low-risk businesses have been proposed, making it easier for new exporters to register and comply with GST without lengthy procedures.
Goods and Services Tax Council
Conclusion: Why Understanding Export GST Rules Is Important
Understanding Export GST rules is not just a legal requirement—it is a crucial part of running a successful and compliant export business in India. These rules are designed to ensure that exporters are not burdened with taxes while supplying goods or services to international markets, but the benefits are available only when the rules are followed correctly.
A clear understanding of Export GST rules helps exporters choose the right export method, whether it is exporting under LUT without payment of tax or exporting with payment of IGST and claiming refunds. It also reduces the risk of errors in documentation, return filing, and refund claims, which are common reasons for delays and notices from tax authorities.
Moreover, staying updated with Export GST rules allows exporters to manage their cash flow better, avoid unnecessary tax payments, and ensure timely receipt of GST refunds. This is especially important for small and medium exporters, where blocked working capital can directly impact business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Export GST Rules
What are Export GST rules in India?
Export GST rules are the provisions under GST law that govern how exports of goods and services are taxed in India. These rules treat exports as zero-rated supplies, meaning exporters can export without GST burden while following prescribed compliance procedures.
Are exports fully exempt from GST under Export GST rules?
No, exports are zero-rated, not exempt. Under Export GST rules, exporters do not charge GST on exports but are allowed to claim refunds of input tax credit or IGST paid, which is not possible in exempt supplies.
What is the difference between exporting with LUT and exporting with IGST?
Under Export GST rules, exporters can export:
Without payment of tax by furnishing a LUT or Bond, or
With payment of IGST and later claim a refund.
LUT is generally preferred as it avoids blocking working capital.
Is LUT mandatory for all exporters?
LUT is not mandatory but highly recommended. As per Export GST rules, if an exporter does not furnish LUT or Bond, they must export with payment of IGST and then claim a refund.
Can a new exporter apply for LUT under Export GST rules?
Yes, new exporters can apply for LUT on the GST portal if they meet eligibility conditions. The Export GST rules allow LUT filing online, and it is usually approved instantly.
How long does it take to receive a GST refund on exports?
As per Export GST rules, GST refunds are generally processed within a prescribed time if all returns are filed correctly and documents are in order. Delays usually occur due to data mismatches or missing documents.
What documents are essential for claiming refund under Export GST rules?
Key documents include export invoices, shipping bills, LUT or Bond, GST returns, and proof of foreign currency realization. Proper documentation is mandatory under Export GST rules to avoid refund rejection.
Do Export GST rules apply to service exporters as well?
Yes, Export GST rules apply to both goods and services. Service exporters must fulfill specific conditions such as receipt of payment in foreign currency and correct place of supply.
What happens if Export GST rules are not followed?
Non-compliance with Export GST rules can lead to refund rejection, interest liability, penalties, and GST notices. Regular compliance helps exporters avoid legal and financial issues.
How often do Export GST rules change?
Export GST rules may be updated through GST Council decisions, notifications, or circulars. Exporters should stay updated to ensure ongoing compliance and benefit from any new relaxations.
