In the modern world, innovation and invention mean economic growth and technological advancement. Nevertheless, such innovations also demand protection and therefore require patents.
A patent provides the inventor or assignee with the sole right to prevent others from making, using, or selling the invention for a certain period of time.
This blog post will dive into the Top 6 types of patents, explaining their significance, how they work, and why they are crucial in various industries.
- What is the Patent?
- Why are Patents very Matters?
- What are the Top 6 Types of Patents?
- How Can You Choose the Right Patent for Your Invention?
- What are the 5 Requirements of a Patent?
- What is the 101 Patent Law?
- In Conclusion
- FAQs
What is the Patent?
Before showing the types of patents, it is very important to know what a patent means. It is defined as a legal right granted by a government authority to an inventor in relation to his new invention and is granted to protect one’s idea or method from others who attempt to use it without permission.
Patents can vary considerably in the breadth of the innovation – for example, from mechanical devices and medicines to software or numerical algorithms used to manage business processes.
In order for the right of exclusivity to prevent others from exploiting the invention, the inventor must provide public access to information relating to the details of the invention so that it is easy for others to learn and innovate further.
If you want to see about the patent then you can click on the below video:
Why are Patents very Matters?

Patents serve several important purposes: Patents serve several important purposes for a reason, and there are so many that we’ve put together a good amount of information on why they matters:
- Innovations are Encouraged: Patents provide the necessary incentive in terms of being able to earn money from the new idea by providing exclusive rights to the inventor.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Patents protect inventors from the nefarious practices of competitors who may develop their creations without permission.
- Boost the Economy: With the commercialization of new technologies and products, patents contribute to overall economic growth.
- Legal Protection: Patents provide legal rights to the inventor against infringement and protect their rights.
What are the Top 6 Types of Patents?

We have mentioned all the top 6 types of patents in a very detailed manner below and also provided good information about each of them individually.
- Utility Patents
- Design Patents
- Plant Patents
- Provisional Patents
- Reissue Patents
- Software Patents
Utility Patents
The most common type of patent is a utility patent. Utility patents are issued for new and useful inventions or discoveries, including processes, machines, manufactured goods, and chemical compositions. They provide powerful protection to practical, industrially useful innovations. Utility patents are of high value as they are highly important due to the strength of the innovation.
Key Features of Utility Patents
- Field of Invention: relates to machines, articles of manufacture, compositions of matter, and processes.
- Term: 20 years from the time of filling in most countries, but with a maintenance fee
- Exclusive Right: Only the patent owner shall have the right to make, use, sell, or offer for sale the invention.
Example: The patent for the iPhone is a utility patent because it covers the technological process and machinery of the device.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Utility Patents
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of utility patents:
| Advantages of Utility Patents | Disadvantages of Utility Patents |
|---|---|
| Strong Protection: Grants exclusive rights for 20 years, allowing for commercialization of the invention. | Complex Application Process: The procedure is detailed and requires extensive documentation and legal compliance. |
| Diversity: Applicable across various industries, including electronics and pharmaceuticals. |
Utility Patent is the 1st type among Top 6 types of patent and also a very important one.
Design Patents
Design patents protect the ornamental design or appearance of a product, but not its functions. Thus, if an object has a shape, pattern, or aesthetic look, others cannot copy or use that design through a design patent.
Key Features of Design Patents
- Scope of invention: Covers only the visual features and overall form of an object.
- Duration: Typically 15 years from the date of grant in the United States (although subject to variation across jurisdictions).
- Exclusivity: Prevents others from copying and/or reproducing the design without permission.
Example: The Coca-Cola bottle’s distinctive shape is protected by a design patent.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Design Patent
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of design patents:
| Advantages of Design Patents | Disadvantages of Design Patents |
|---|---|
| Fast Application: The application process is shorter and less complex than for utility patents. | Focus on Aesthetics: Primarily protects unique beauty, making it more suitable for branding and design rather than functionality. |
| Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive to file and maintain compared to utility patents. | Narrow Scope: Does not cover functionality; protects only the form or appearance of an object. |
Design Patent is the 2nd type among Top 6 types of patent and also a very important one.
If you also want to do patent registration then you can get a complete guide to this just by clicking here
Plant Patents
A plant patent can be issued to any inventor who discovers or reproduces a new and distinct variety of plants. Plant patents are more used in agriculture and horticulture, especially on genetically modified plants or those with special characteristics including resistance to diseases and higher yield.
Key Features of Plant Patents
- Scope of Invention: Newly reproducible plant varieties in an asexual manner with exceptions in tuber propagated plants.
- Duration: 20 years from the date of filing.
- Exclusivity: Any other individual cannot propagate or distribute the patented variety of plants without permission.
Example: A patent for a newly developed hybrid of roses would be classified as a plant patent.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Plant Patent
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of plant patents:
| Advantages of Plant Patents | Disadvantages of Plant Patents |
|---|---|
| Promotes Agricultural Innovation: Encourages research and development in plant breeding. | Narrow Application: Limited to vegetative reproduction; its applicability is confined. |
| Legal Protection: Provides legal immunity for new varieties to growers and breeders. |
Plant Patent is the 3rd type among Top 6 types of patent and also a very important one.
Provisional Patents
A provisional patent issues an early filing date for an invention in the form of a temporary patent application. Although not a full patent, a provisional patent allows inventors 12 months to continue the development of their invention while preparing a formal patent application.
Key Features of Provisional Patents:
- Scope of invention: It temporarily covers all types of inventions covered by utility patents but without full protection under the law.
- Period of protection: It lasts 12 months, by the end of which the inventor must apply for a non-provisional patent.
- Privileges: While providing a “patent pending” status, it gives the invention no enforceable patent rights.
Example: Even an inventor who is in the stage of developing an innovative new software system can file a provisional patent to get a filing date while he or she perfects his or her product.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Provisional Patent
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of provisional patents:
| Advantages of Provisional Patents | Disadvantages of Provisional Patents |
|---|---|
| Cost: Lower filing costs and easier application process compared to full patents. | Temporary Protection: Provides only temporary protection; must be followed by a formal patent application. |
| Flexibility: Allows inventors time to develop their invention while securing an early filing date. |
Provisional Patent is the 4th type among Top 6 types of patent and also a very important one.
Reissue Patents
Reissue patents are granted when a patent appears to be faulty or incomplete after it is issued. The patent holder can apply for a reissue to correct a mistake so that the issued patent accurately reflects the invention. Reissue patents can correct matters such as errors relating to the scope or claims of the patent.
Key Features of Reissue Patents
- Scope of invention: Applies to inventions already patented, but whose description needs correction.
- Duration: Does not extend the original patent term.
- Exclusivity: This provides the same protection as the original patent.
Example: A company discovers that there is an error in the claims of its original patent; it can seek a reissue patent to correct that error.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reissue Patent
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of reissue patents:
| Advantages of Reissue Patents | Disadvantages of Reissue Patents |
|---|---|
| Error Correction: Allows patent owners to correct errors in the original patent. | No Term Extension: Does not extend the original patent term; it still expires on the original date. |
| Validity: Ensures the invention receives the correct legal protection. | Complexity of the Process: The application process can be complicated and may require legal assistance. |
Reissue Patent is the 5th type among Top 6 types of patent and also a very important one.
Software Patents
Patents on software have become of vital importance as the last two decades have witnessed technology at the center of modern business life, and later, modern daily life. Software patents ensure protection over the code, processes, and algorithms in developing a software product.
Key Features of Software Patents:
- Invention scope: It includes software algorithms, processes, and applications.
- Duration: Generally, it is 20 years from the date of filing.
- Exclusivity: Software Patents prohibit any unauthorized person or entity from using or copying the patented software.
Example: A new encryption algorithm can be covered by a patent on software.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Software Patent
Here’s a table summarizing the advantages and disadvantages of software patents:
| Advantages of Software Patents | Disadvantages of Software Patents |
|---|---|
| Venerate Innovations in Tech: Provides legal protection for valuable software innovations. | Controversy: Can stifle innovation by locking up basic algorithms and techniques. |
| Promote Technological Advancement: Encourages the protection of algorithms and code, facilitating progress in the technology sector. | Difficult to Enforce: Proving infringement can be more challenging compared to other types of patents. |
Reissue Patent is the 6th type among Top 6 types of patent and also a very important one.
If you want to see about the top 6 types of patent then you can click on the below video:
How Can You Choose the Right Patent for Your Invention?

There are different types of patents, and the kind of patent chosen will depend on the nature of the invention. Utility patents will be most appropriate if new products or processes are discovered. Design patents will cover improvements related to the appearance of a product.
If the innovation refers to new plant varieties, it falls under plant patents, and if it is software, software patents apply.
When you haven’t filed a full patent yet, a provisional patent can serve as your safety net; it can be used pending the finalization of your invention. If you find errors in your original patent, you can always apply for a reissue patent to correct the mistake.
What are the 5 Requirements of a Patent?
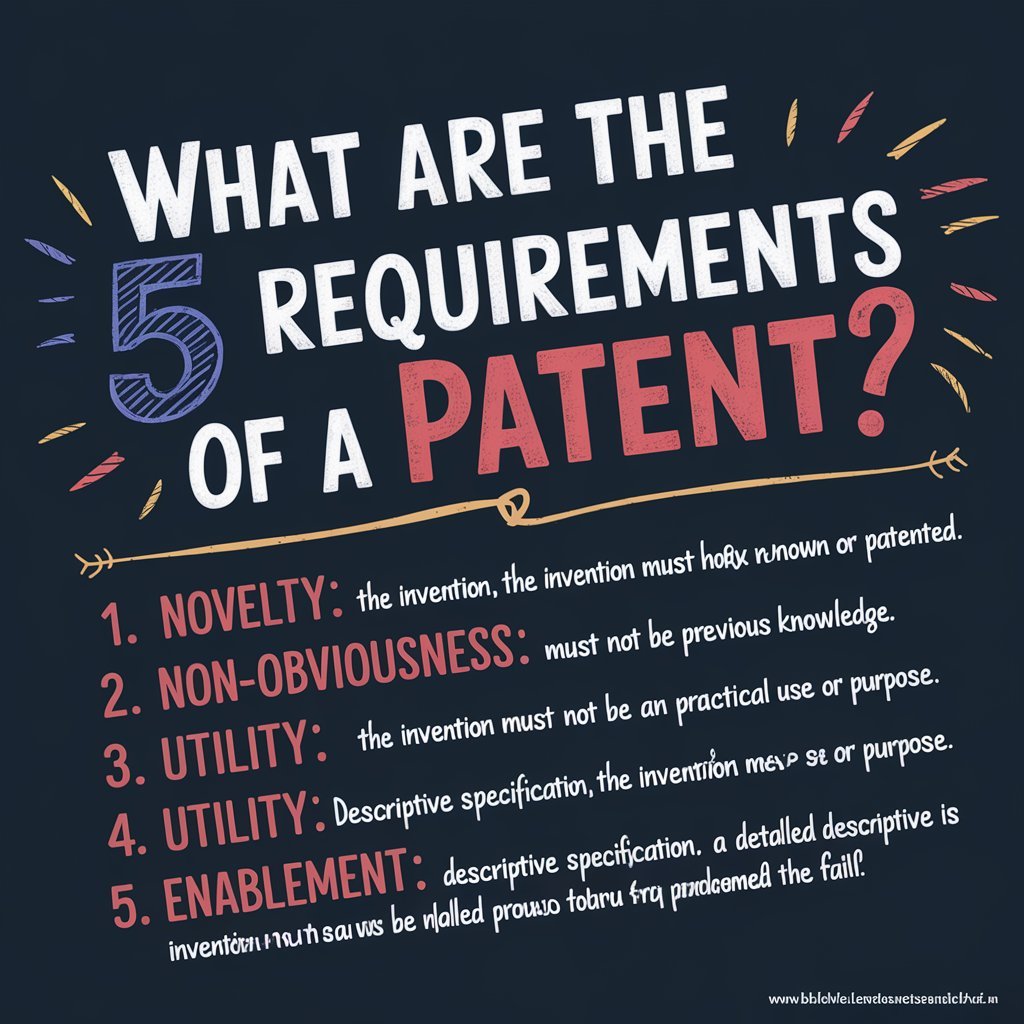
To be patentable, an invention must meet five major criteria. These requirements are meant to ensure that only novel, useful, and well-defined inventions receive the validity of protection. Below is a general overview of these five essential requirements.
- Patentable subject matter: This relates to one of the categories of patentable inventions: machines, processes, or compositions of matter.
- Novelty: The invention must be new, not known, or not used publicly before filing an application for a patent.
- Non-obviousness: Such inventions may not be obvious to those who have experience in the field; they must be something new.
- (Utility): The invention must have utility and provide some practical benefit in real life.
- Adequate description (Enablement): The invention must be described in the patent application in such a way that other people are able to understand it and make it.
What is the 101 Patent Law?
Section 101 of the U.S. Patent Law mentions what types of inventions can or cannot be patented. According to this, the invention of any new and useful process, machine, manufacture, or composition of matter, or any improvement thereof, is patentable, in addition to all other statutory requirements (novelty and non-obviousness). Under this section, laws of nature, abstract ideas, and natural phenomena are reserved for non-patentability.
In Conclusion

Understanding the different types of patents, and each of these patents must be clearly understood to protect any intellectual property. Whether you design a novel technological innovation, come up with a new unique product, or introduce a new variety of plants, there will definitely be a patent that is designed to protect your work.
The correct filing of a patent ensures that your invention is protected as well as gives you the exclusive right to commercially exploit that particular invention. Taking the time to understand the types of patents and how it applies to your innovation is probably a big key to your success in that competitive world of innovation.
FAQs
Q1. What is the most common type of patent?
The most common type of patent is the utility patent, which protects new and useful inventions such as processes, machines, or compositions of matter.
Q2. Is copyright a type of patent?
No, copyright and patents are different forms of intellectual property protection. Copyright protects creative works like books, music, and art, while patents protect inventions and designs.
Q3. Do patents expire?
Yes, patents expire. Utility and plant patents last for 20 years from the filing date, while design patents last for 15 years.
Q4. What are patents 3 examples?
Examples of patents include:
A new pharmaceutical drug (utility patent)
The ornamental design of a chair (design patent)
A new apple tree variety (plant patent).
Q5. What are the three types of patents in India?
The three types of patents in India are: utility patents, design patents, and plant patents.
Q6. Who issues patents?
Patents are issued by national or regional patent offices, such as the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) in the U.S. or the Indian Patent Office in India.


Add a Comment